Phenylalanine N-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.40, phenylalanine N-hydroxylase, CYP79A2) is an enzyme with systematic name L-phenylalanine,NADPH:oxygen oxidoreductase (N-hydroxylating). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
- L-phenylalanine 2 O2 2 NADPH 2 H (E)-phenylacetaldoxime 2 NADP CO2 3 H2O (overall reaction)
- (1a) L-phenylalanine O2 NADPH H N-hydroxy-L-phenylalanine NADP H2O:
- (1b) N-hydroxy-L-phenylalanine O2 NADPH H N,N-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine NADP H2O
- (1c) N,N-dihydroxy-L-phenylalanine (E)-phenylacetaldoxime CO2 H2O
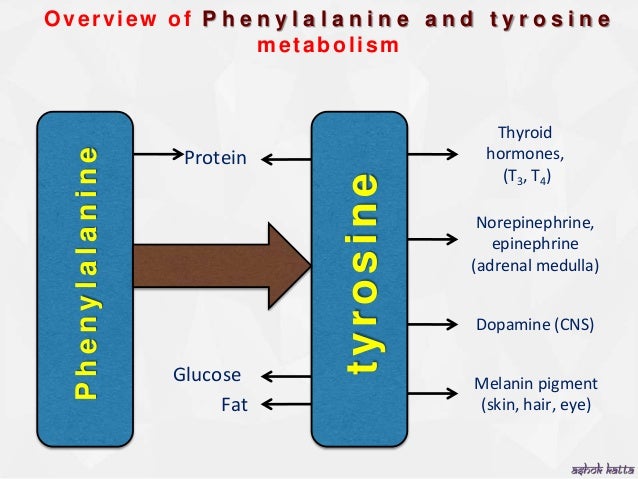
Phenylalanine N-monooxygenase is a heme-thiolate protein (P-450). It is part of the pathway in plants which converts phenylalanine to the glucosinolate, glucotropaeolin, which contributes to the characteristic flavor of brassicas.
References
External links
- Phenylalanine N-monooxygenase at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)